-
- Daily Resources and Learning Intentions Daily Resources and Learning Intentions
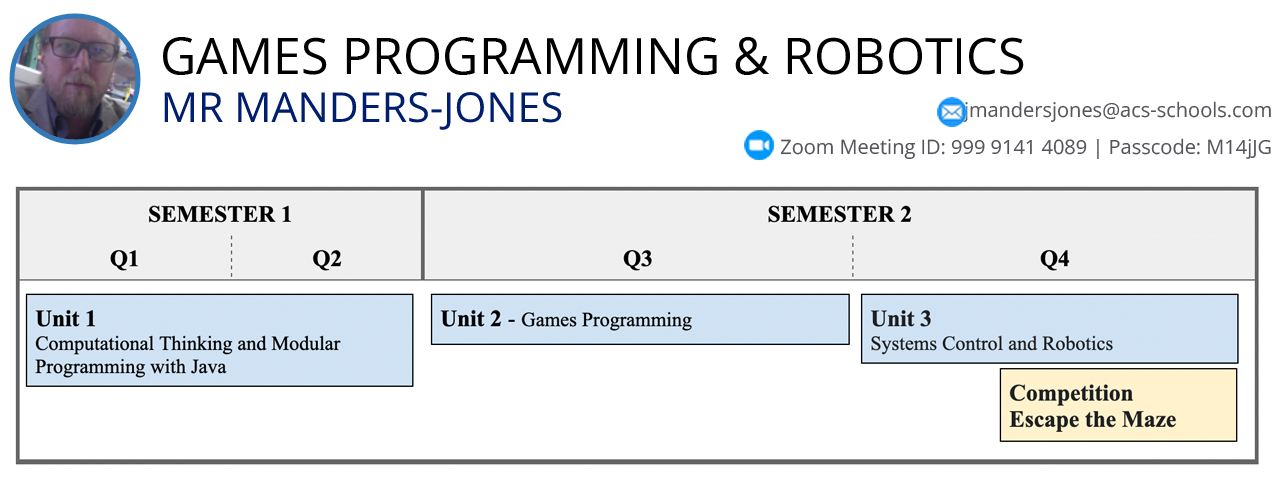
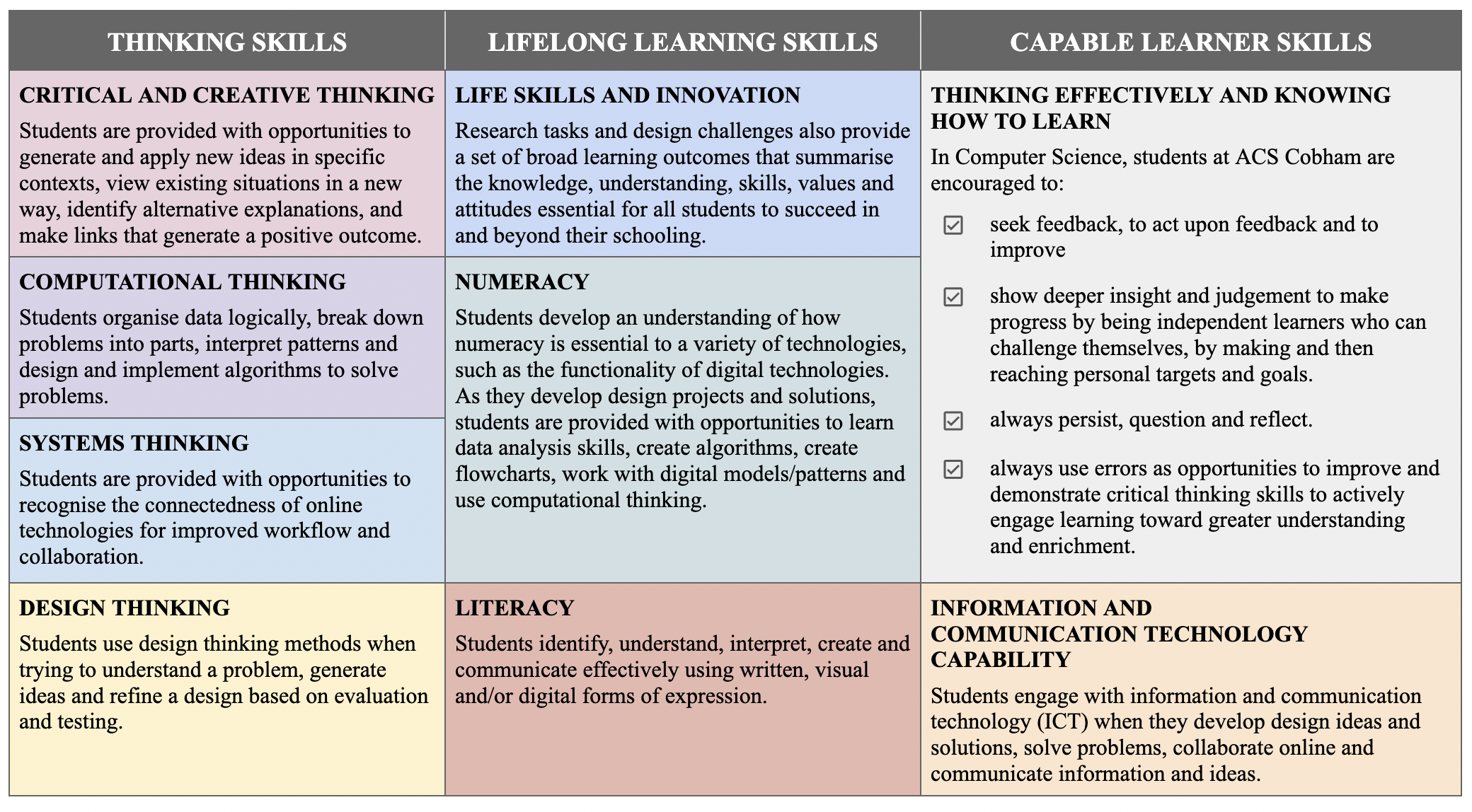
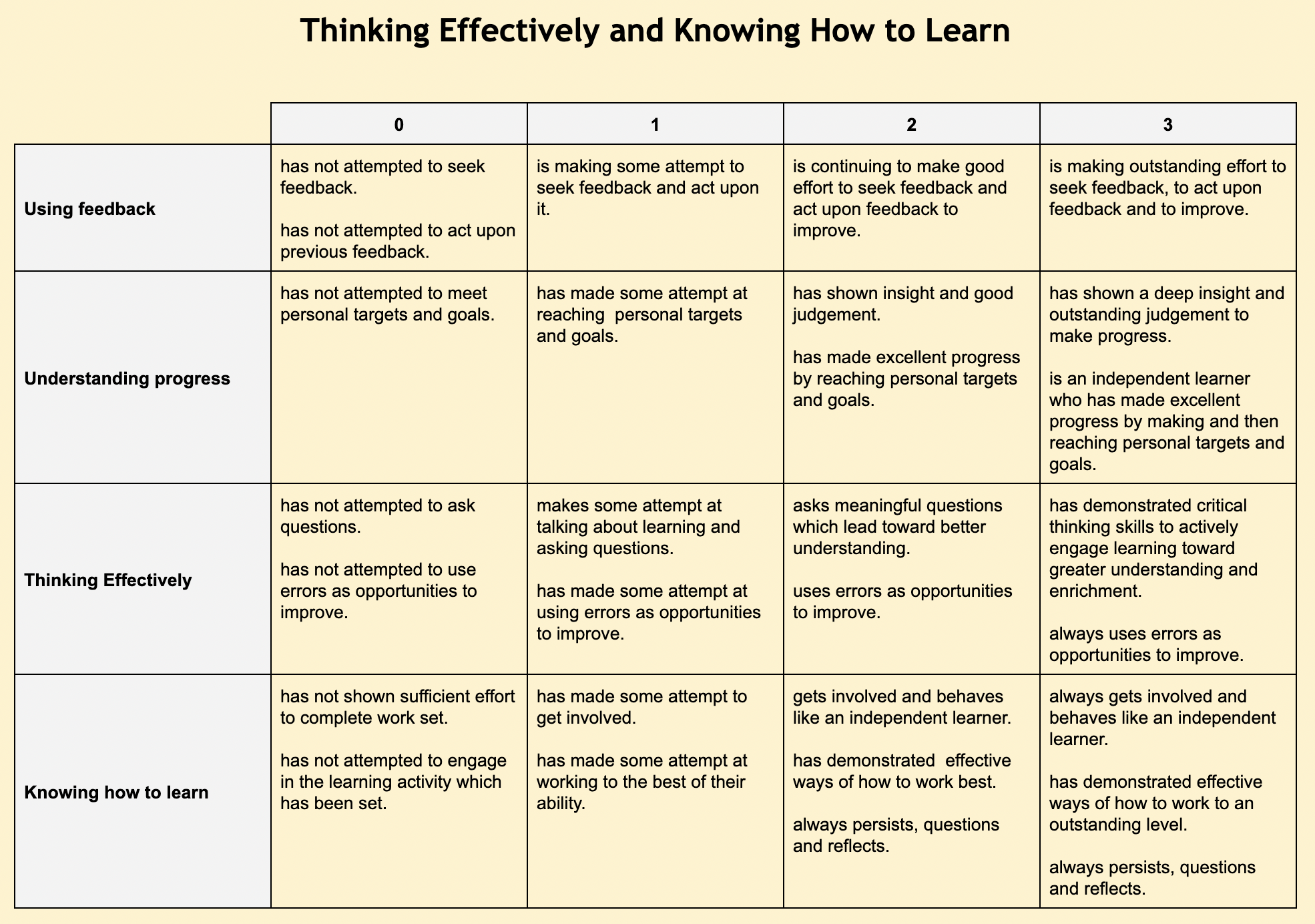
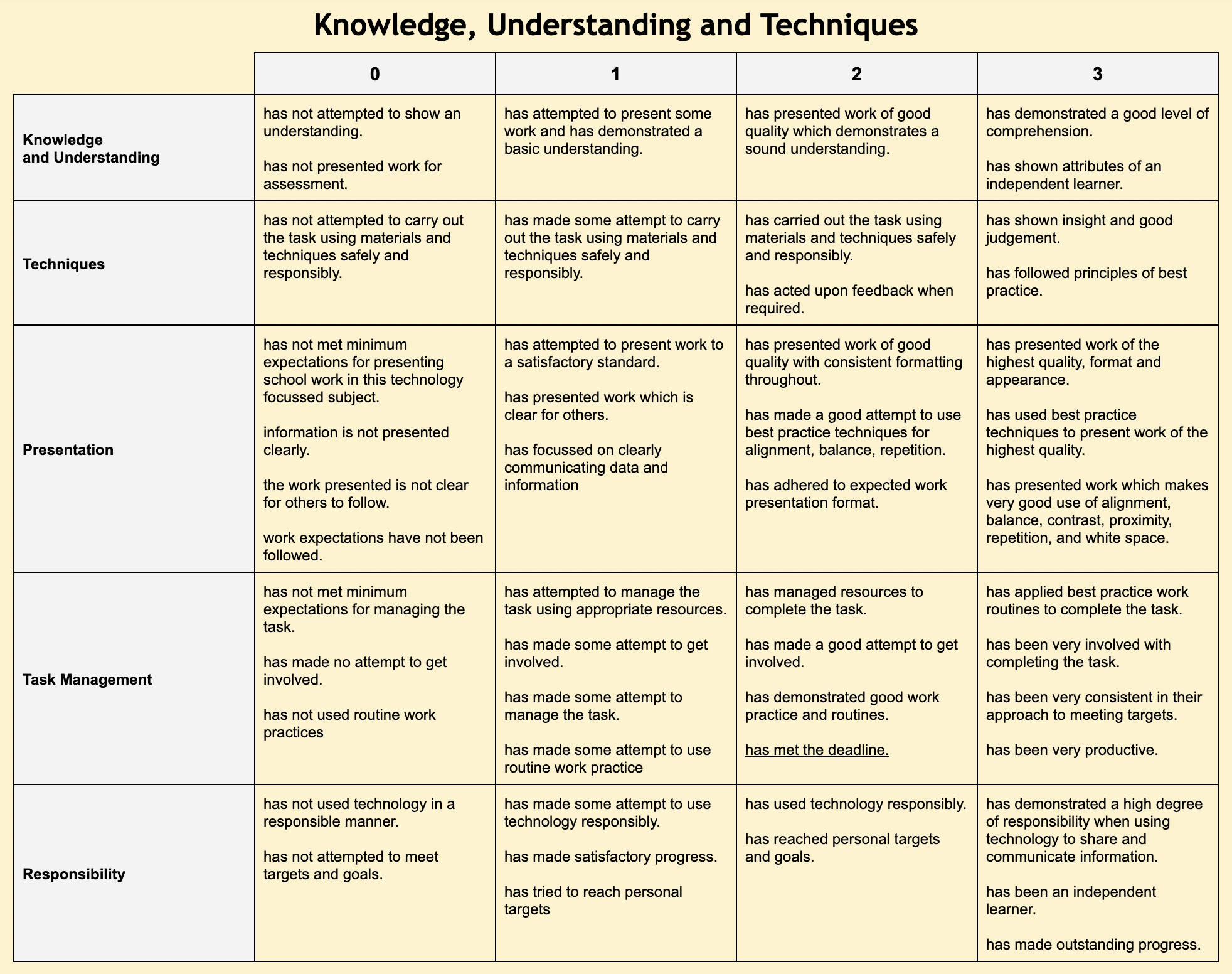
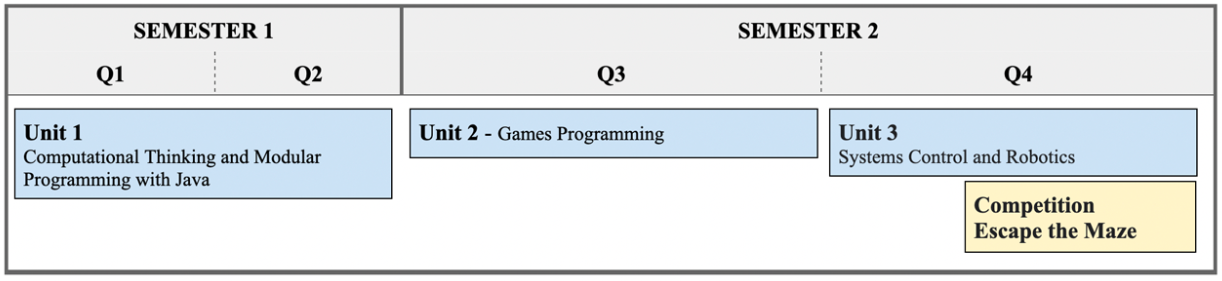
- Course Overview & Assessment Course Overview & Assessment
- Unit 1 - Computational Thinking and Java Programming Unit 1 - Computational Thinking and Java Programming
- Unit 1 - Data Representation and Logic Programming using Conditionals Unit 1 - Data Representation and Logic Programming using Conditionals
- Unit 2 - Games Programming & Computer Graphics Unit 2 - Games Programming & Computer Graphics
- Unit 3 - Robotics & Control Systems Unit 3 - Robotics & Control Systems